|
The
PoLoS project aims to design specify and implement an Integrated Platform, which
will cater for the full range of issues concerning the provision of Location
Based Services (LBS). This platform will enable the specification, creation and
deployment of such services within the premises of service operators, without
any additional requirement in terms of network platforms or terminal devices.
The Unified Modeling Language (UML) will be used for defining the PoLoS
architectural and functional aspects. Languages like SDL may also be utilised if
relevant need arises.
The
PoLoS platform will provide the full functionality needed by both the Service
Operator, which will deploy the location based service, as well as the end user,
who will take advantage of the deployed service. To achieve this functionality,
the PoLoS platform will feature a component-based architecture. Each component
within this modular architecture will have a specific and clearly defined
functionality. The two main entities defined within the PoLoS platform are the
PoLoS Kernel and the Peripheral Components. The overall architecture of the
pursued platform is shown in Figure
2
.
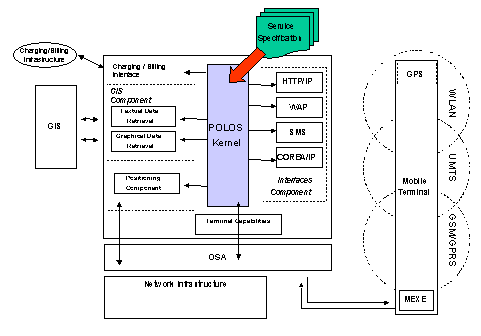
Figure
2:
Target Architecture
Moreover,
within the scope of the project is the development of a Service Creation
Environment (SCE) for creating location-based services. More details on these
environment is provided in following paragraphs.
PoLoS
kernel
The
PoLoS kernel comprises the primary component of the pursued platform. It will be
developed using java-based technologies (e.g. JAVA, J2EE) and its functionality
will be the co-ordination of the rest of the components in order to provide the
functionality specified for each location-based service. Moreover, the PoLoS
architecture will feature an interface, which will allow the PoLoS kernel to
determine the capabilities of the mobile terminal. This interface will
capitalise on the MExE technology.
Three
peripheral components are clearly identified within the PoLoS architecture:
1.
The GIS component
2.
The Positioning component
3.
The Interfaces component
Each
of the above mentioned components is responsible for providing a certain
function within the PoLoS platform. Communication between the components if
required will be made through the kernel. Furthermore communication between the
kernel and the peripheral components can be based either on XML formatted
messages or implemented through well-defined APIs.
The
GIS Component is responsible for the interaction with deployed GIS repositories.
It may include various software modules, as shown in Figure
2 to cover both visual as well as textual information. The purpose of
these modules will be the exploitation of the wealth of information stored in
GIS servers in order to create a graphical representation (e.g. map) of the area,
where a specific service is going to be deployed.
The
GIS Component will be invoked by the PoLoS kernel whenever necessary in order to
provide the information needed for the provision of a certain service. This
information can be used either internally (by the kernel or another component)
or be transmitted to the mobile terminal (e.g., a graphics file) as part of the
information provided by the specified service. A protocol between the GIS
component and the GIS repository will be developed, possibly by exploiting the
capabilities of XML. Such protocol will signal the information requirements of
the Kernel to the remote end and retrieve information as needed.
The
Positioning Component will be responsible for providing the PoLoS kernel with
the appropriate information pertaining to the position of a mobile terminal
accessing a particular service. In order to acquire this information the
component will use available positioning techniques provided by the underlying
network. Determining the position of a mobile terminal can be based either on
satellite-based systems (e.g. GPS), terrestrial infrastructure-based systems (e.g.
TOA, E-OTD) or hybrid systems (e.g. D-GPS). Access to the network will be
implemented through the OSA interface. Furthermore, special provision will be
taken to (alternatively) interface the system to 3G network components like the
Gateway Mobile Location Center (GMLC) as they become available in the
operatorís infrastructure.
The
Interfaces Component is responsible for communicating the service specific
information to the mobile terminal. The interface will support different
transport protocols from SMS and WAP to IP and the PoLoS kernel will invoke the
appropriate, for each terminal, protocol in order to transmit service specific
information to the terminal. Depending on the capabilities of the terminal and
the requirements of the location based service to be accessed information
exchanged could vary from simple textual data to downloading of small software
modules in order to be executed in the environment of the mobile terminal (i.e.
using MExE). Additionally, depending on the technology used by the terminal,
protocols could be extended to accommodate geographical information (e.g.,
similarly to the longitude/latitude elements introduced in the so-called Dynamic
URL scheme).
Service
Creation Environment
Development
of the Service Creation Environment (SCE) will focus on the design of an
appropriate service specification language, a language capable to support the
description of the functionality pertaining to each service. This language will
be based on analogous languages that exist today hence it is highly probable
that it will capitalize on the XML technology. The language will be flexible,
and easy to use in order to allow for the specification and easy deployment of
any type of LBS without too much effort and cost from the service provider. Each
service will be defined through scripts written in this new language. Such
scripts will run in the PoLoS kernel, which in turn will invoke the peripheral
components, in order to provide the functionality needed for each service. To
render the use of the language as efficient as possible, the project will also
pursue the design of an integrated development environment (IDE) that will
greatly facilitate the development and deployment of new services.
|